
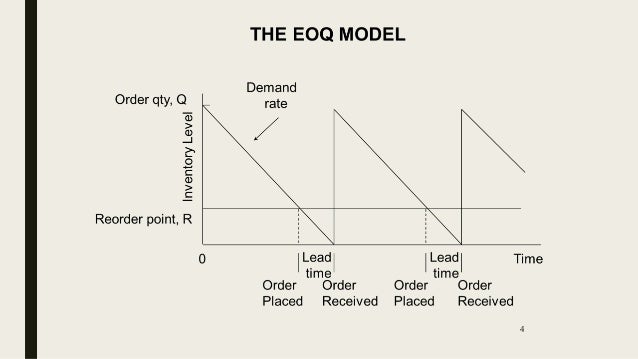
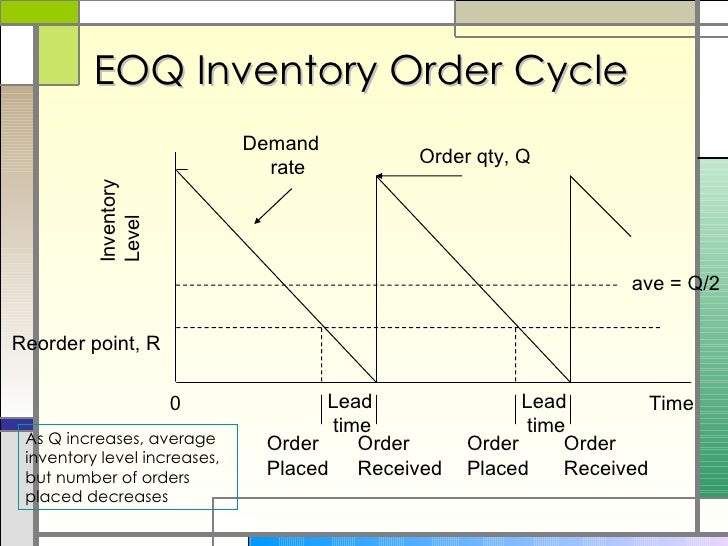
Lead time is constant: EOQ assumes a consistent lead time, which is the time between placing an order and receiving the inventory.This assumption implies that demand does not fluctuate or vary significantly during the lead time. Demand is constant and known: EOQ assumes that the demand for the product is constant over the ordering period and is accurately known in advance.The EOQ model is based on several assumptions, including:
The basic formula for calculating Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is as follows:ĮOQ = Economic Order Quantity (optimal order quantity)Īssumptions of Economic Order Quantity ( EOQ): By determining the optimal order quantity, organizations can avoid excessive inventory carrying costs while ensuring an adequate stock level to meet customer demand.įormulas for Economic Order Quantity ( EOQ): The primary objective of EOQ is to identify the order quantity that minimizes the total cost of inventory, taking into account both holding costs and ordering costs. Ordering costs, on the other hand, are the expenses associated with placing and receiving orders, such as administrative costs, transportation, and setup costs. Holding costs refer to the expenses incurred for storing and managing inventory, including warehousing, insurance, obsolescence, and capital costs. The concept of Economic Order Quantity is based on the trade-off between two types of inventory costs: holding costs and ordering costs. In this explanation, we will delve into the concept, formulas, assumptions, benefits, and considerations of Economic Order Quantity. EOQ provides insights into the frequency and quantity of orders to optimize inventory levels, reduce holding costs, and enhance operational efficiency. It helps organizations strike a balance between the costs associated with holding inventory and the costs of ordering or replenishing inventory. Economic Order Quantity ( EOQ) is a mathematical model used in inventory management to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
